Context
This mixed engineering structure, composed of cut-stone masonry vaults later widened by a concrete structure, is subjected to significant daily loads.
The appearance of a longitudinal crack at the crown of the vault on one of the spans led the asset owner to request an in-depth assessment.
The objective of the assignment was twofold: to go beyond a simple visual inspection in order to characterise the actual structural response under traffic loading, and to provide objective data to guide the maintenance strategy.
Interventions carried out
To establish this structural diagnosis, CIDECO implemented a hybrid approach:
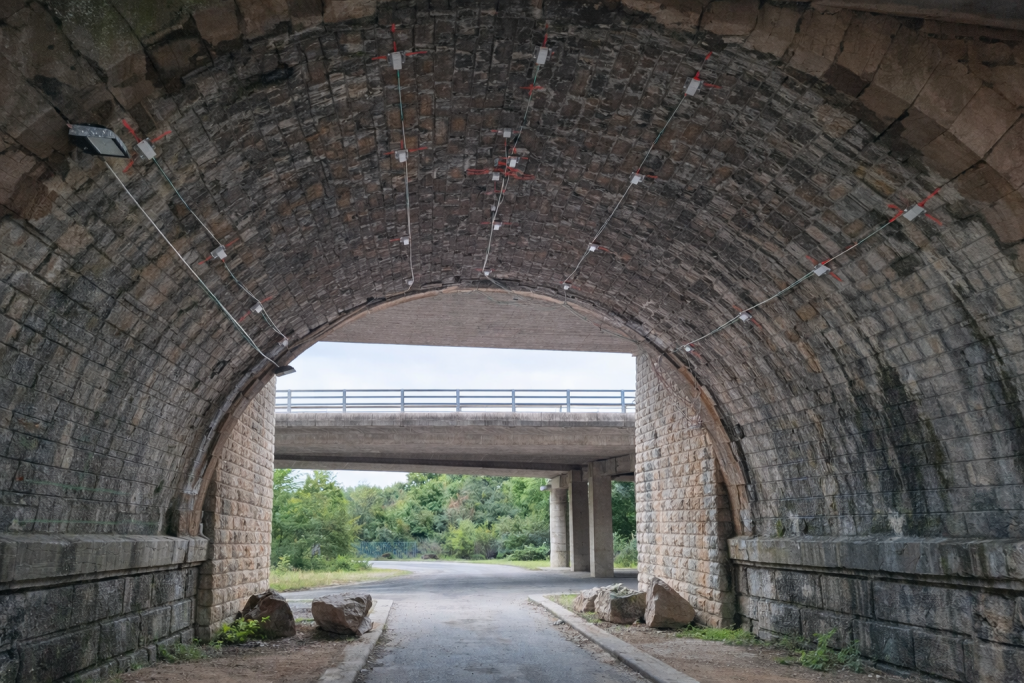
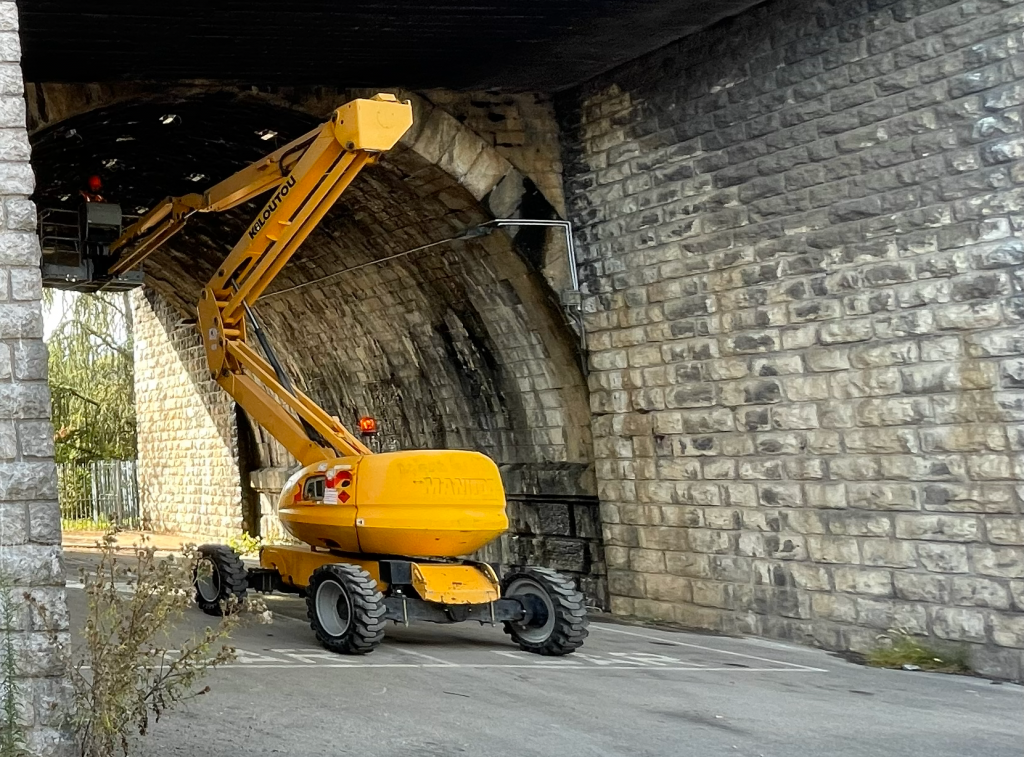
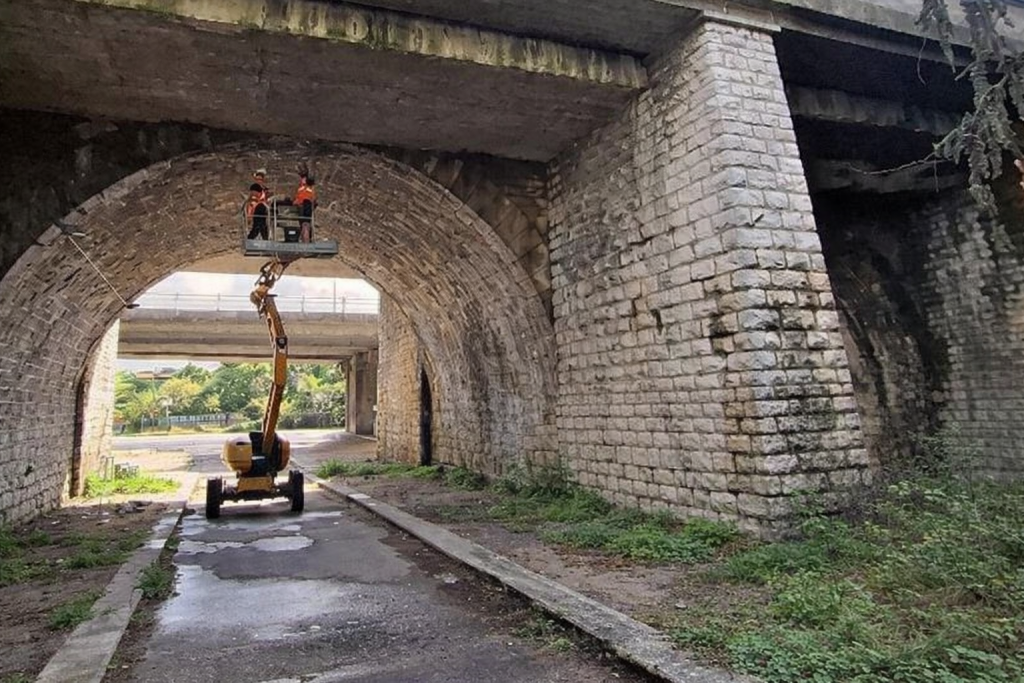
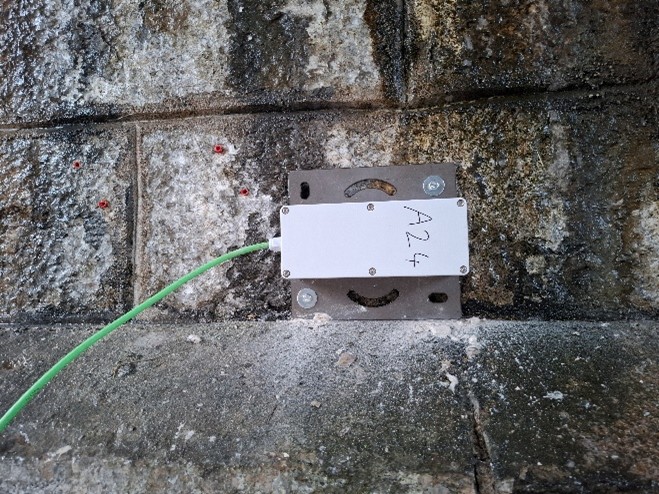
- Advanced instrumentation: Deployment of a network of connected sensors on three spans (the cracked area and two sound reference areas).
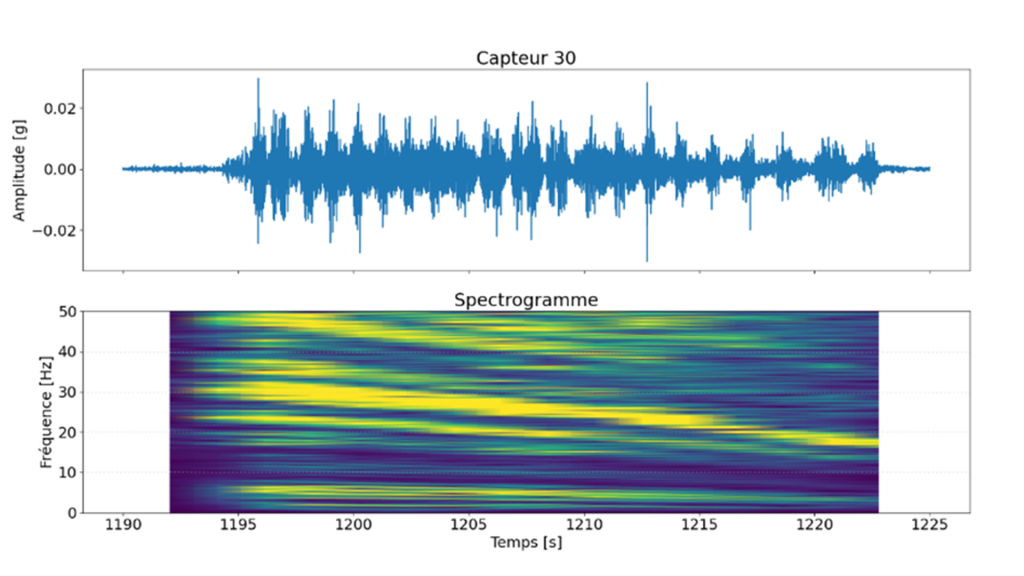
3D MEMS accelerometers and induction crack gauges recorded the structural kinematics at high frequency (1000 Hz) under various loading cycles.
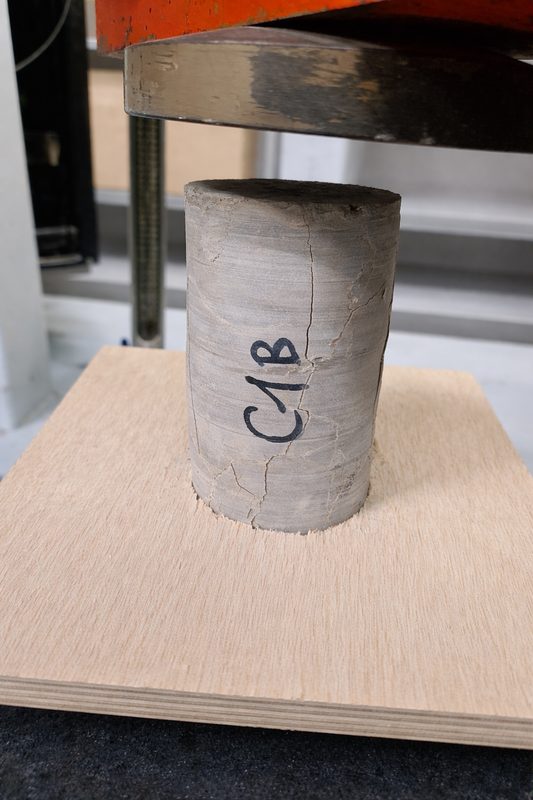
- Material characterisation: Core drilling investigations and endoscopic inspections were carried out to verify the internal compactness of the masonry.
Laboratory compression tests made it possible to validate the assumptions regarding the mechanical strength of the stone.
Methods and expertise mobilised
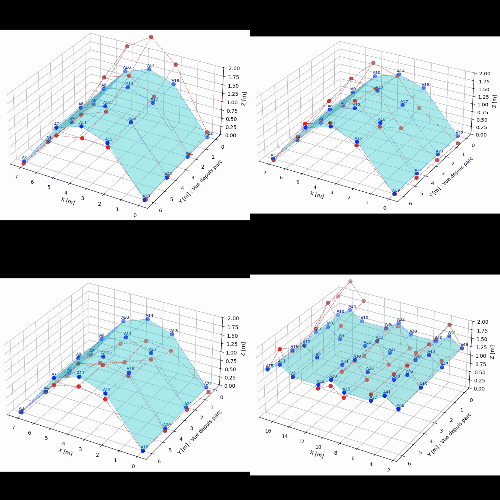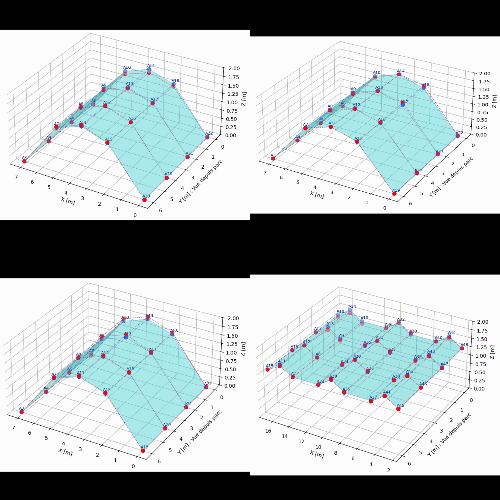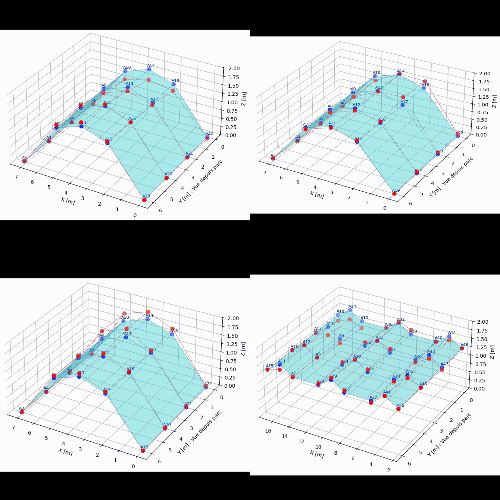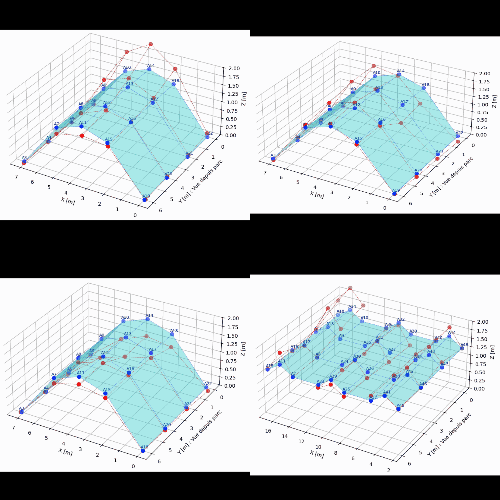
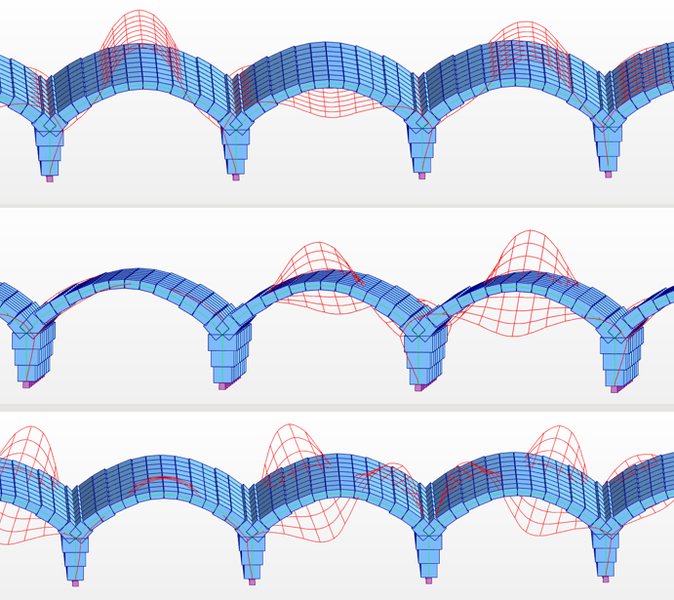
The application of an Operational Modal Analysis (OMA) made it possible to identify the natural modes of the structure (bending, torsion) within a frequency range of 15 to 31 Hz.
The results highlighted a specific signature for the damaged vault: a reduction in natural frequencies and an increased dispersion of the results, which are characteristic symptoms of a non-linear and dissipative behaviour associated with the crack.
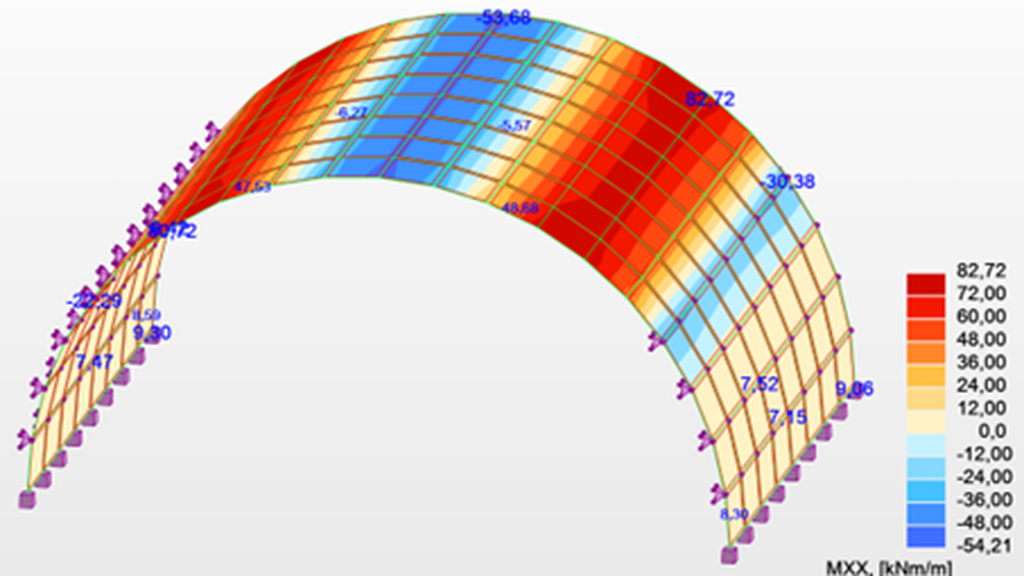
These field data were then used to feed a finite element calculation model.
This digital twin, calibrated against real measurements, validated the consistency between the physical observations and the theoretical behaviour of the arch.
Added value
This study demonstrated that vibrational diagnosis is a powerful decision-support tool.
While the materials retain high mechanical performance, the diagnosis objectively highlighted the need for increased monitoring of the cracked area.
Thanks to this calibrated model (Digital Twin), the Project Owner was able to avoid an unnecessary preventive closure and implement targeted monitoring only on critical areas.